Discovery with the support of the ORP TA - international team of researchers have detected cold molecular gas in the form of carbon monoxide in the host galaxy of a supermassive black hole at an early epoch in cosmic history
Using the transnational access funded by the EC granted Opticon RadioNet Pilot project, Astronomers have detected cold molecular gas in the form of carbon monoxide in the host galaxy of a supermassive black hole at an early epoch in cosmic history, corresponding to when the Universe was only seven hundred million years old. The discovery was made by an international team led by researchers from the Italian National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) using the NOEMA observatory in the French Alps. The results are published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters under the title First Constraints on Dense Molecular Gas at z = 7.5149 from the Quasar Pōniuā'ena. Read here the IRAM news release.
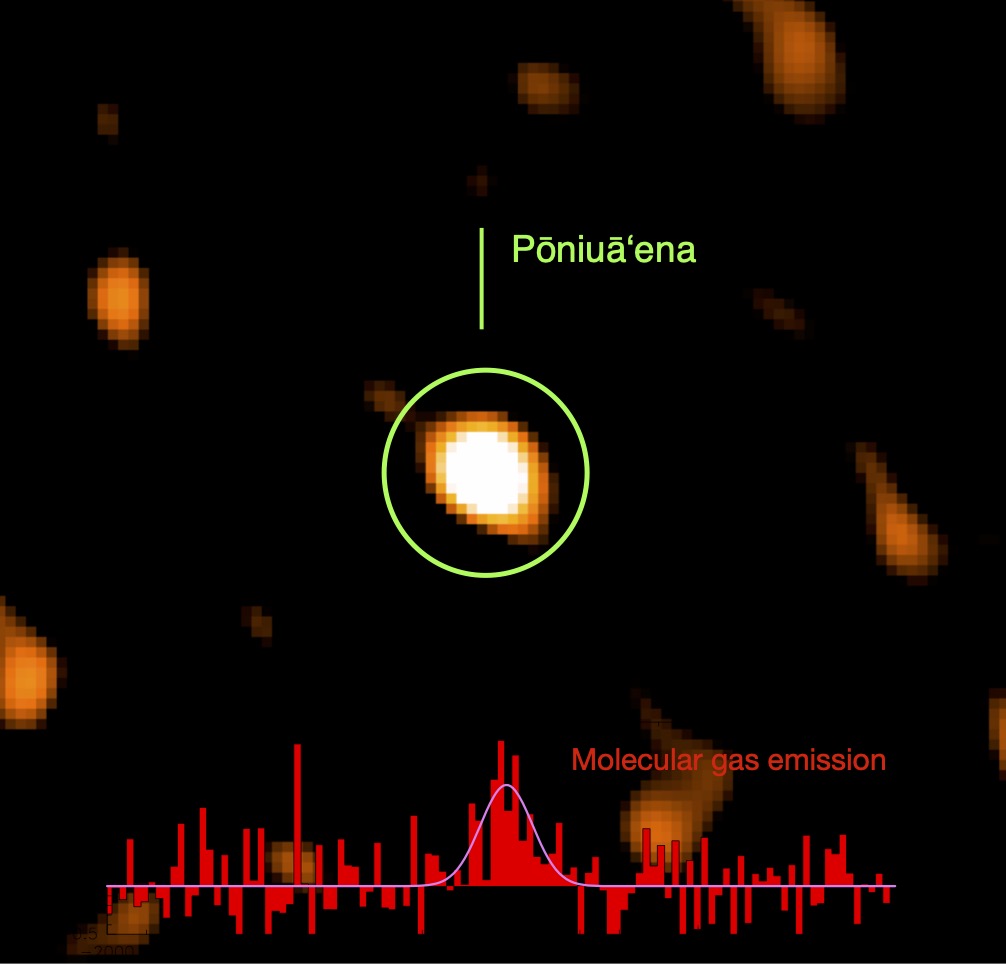
Image: © IRAM/NOEMA/C. Feruglio (INAF); Map of the molecular gas (carbon monoxide) emission from the Poniua‘ena quasar, obtained with NOEMA. In the lower part of the image, the emission line detection.